BECE 2003 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The method used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid is
Solution: Filtration is the process that separates an insoluble solid from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter medium that traps the solid particles.
2. The scent of a perfume sprayed at one corner of a room fills the entire room through
Solution: Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, allowing perfume scent to spread throughout the room.
3. Which of the following processes is a physical change?
Solution: Solidification of water into ice is a physical change because it is reversible and does not alter the chemical composition of water.
4. Atoms of the same element have the same
I. number of electrons
II. number of protons
III. chemical properties.
Which of the above statements are true?
Solution: Atoms of the same element have identical protons (defining the element), electrons (in neutral atoms), and thus identical chemical properties.
5. The unit of measurement of energy is
Solution: The joule is the SI unit for energy, named after James Prescott Joule, and measures work/energy transfer.
6. Which of the following energy transformations takes place at a hydroelectric power station?
Solution: Water at height has potential energy, converted to kinetic energy as it flows down, then to electrical energy via turbines and generators.
7. A drawing of magnetic lines of force provides information on the
Solution: Closer magnetic field lines indicate stronger fields, while wider spacing indicates weaker fields.
8. A bottle of water removed from a refrigerator soon becomes covered with droplets of water because the
Solution: Warm, moist air contacts the cold bottle, causing water vapor to condense into droplets on the cooler surface.
9. The volume of a metal ball was determined by dropping it into a measuring cylinder containing 20 cm\(^3\) of water and the water level rose to 35 cm\(^3\). If the mass of the ball is 35 g, calculate its density.
Solution: Density = mass/volume. Volume = 35 cm³ - 20 cm³ = 15 cm³; Density = 35g / 15cm³ ≈ 2.33 g/cm³ (rounded to 2.3 g/cm³).
10. A boy stepped on a banana peel on the ground and fell because the
Solution: The banana peel reduces friction between the shoe and ground, causing loss of traction and slipping.
11. Which of the following conditions describes a first class lever?
Solution: In a first-class lever (e.g., seesaw), the fulcrum (pivot) is positioned between the effort and load.
12. A man did 75 J of work by lifting a 50 N load from the floor on to a shelf. Calculate the height of the shelf
Solution: Work = force × distance; 75 J = 50 N × height; Height = 75 J / 50 N = 1.5 m.
13. The lion is a carnivore because it eats
Solution: Carnivores are animals that primarily consume the flesh/meat of other animals.
14. The structure which helps a fish to breathe under water is the
Solution: Gills extract dissolved oxygen from water and expel carbon dioxide, enabling underwater respiration.
15. The thorns found on some plants are used for
Solution: Thorns are modified structures that deter herbivores and protect the plant from physical damage.
16. The following characteristics are features of all living things except ability to
Solution: Not all living things move (e.g., plants), but all reproduce, excrete, and grow.
17. Which of the following parasites lives on field animals
Solution: Ticks are external parasites that attach to the skin of animals (e.g., cattle) to feed on blood.
18. The greatest danger faced by mammals living on land is
Solution: Water loss via evaporation (respiration/sweating) is a major survival challenge for terrestrial mammals.
19. The insect responsible for the spread of malaria is the
Solution: Female Anopheles mosquitoes transmit Plasmodium parasites to humans through bites, causing malaria.
20. Which of the following substances is added to the soil to reduce its acidity?
Solution: Lime (calcium carbonate) neutralizes acidic soil by reacting with hydrogen ions to raise pH.
Fig. 1 shows the arrangement of parts of the soil when some soil sample was shaken with water in a glass cylinder and allowed to settle. Use it to answer Questions 21 and 22
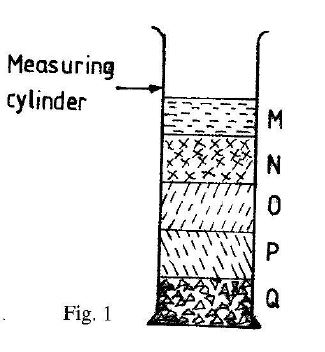
21. Which of the labeled layers contains organic matter?
Solution: Layer M (topmost) contains lightweight organic matter like decomposed leaves that float on water.
22. The layer which does not have the ability to retain much water is
Solution: Layer Q (sand) has large particles with low surface area, resulting in poor water retention.
23. Which of the following characteristics applies to only plants?
Solution: Only plants perform photosynthesis, converting CO₂, water, and sunlight into glucose and oxygen.
24. The waste products of respiration are
Solution: Aerobic respiration produces CO₂ and water as waste: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + energy.
25. The function of the lung is to
Solution: Lungs expel CO₂ (waste from metabolism) from the blood into exhaled air during respiration.
26. Which of the following plants reproduce(s) vegetatively?
I. Banana
II. Mango
III. Ginger
Solution: Banana (suckers) and ginger (rhizomes) reproduce asexually via vegetative structures; mango uses seeds.
27. The process which takes place in all living cells is
Solution: Respiration occurs in all living cells to release energy (ATP) from nutrients for metabolic processes.
28. The food substance found in yam is
Solution: Yam is a tuber rich in starch (complex carbohydrate), providing energy storage for the plant.
29. The end-products of the digestion of fats and oils are
Solution: Lipase enzymes break down fats/oils into fatty acids and glycerol for absorption in the small intestine.
30. Which of the following factors promote plant germination?
I. Adequate temperature
II. Moisture
III. Good soil.
Solution: Germination requires water (to activate enzymes) and optimal temperature; soil is not essential (e.g., hydroponics).
31. The female part of a flower is the
Solution: The pistil (stigma, style, ovary) contains ovules and receives pollen for fertilization in flowering plants.
32. Which of the following substances breaks down fats into tiny droplets during digestion
Solution: Bile emulsifies fats into smaller droplets, increasing surface area for lipase enzymes to act efficiently.
33. Blood in the urine is a symptom of
Solution: Bilharzia (schistosomiasis) damages urinary tract blood vessels, causing hematuria (blood in urine).
34. A free movement of the bowels is aided by
Solution: Dietary fiber adds bulk to stool, softens it, and stimulates peristalsis for regular bowel movements.
35. Which of the following diseases is spread through the air?
Solution: Measles spreads via airborne respiratory droplets from coughs/sneezes of infected individuals.
36. How many days in a month does the moon appear?
Solution: The moon’s synodic cycle (phases) lasts ~28 days, making it visible throughout the month.
37. The earth moves completely round the sun once in every
Solution: Earth completes one revolution around the sun in 365 days (1 year), defining our calendar.
38. A smaller heavenly body, which orbits a bigger one could be described as a
Solution: A moon (natural satellite) orbits planets; e.g., Earth’s moon orbits our planet.
39. Which of the following parasites is a plant?
Solution: Dodder (Cuscuta) is a parasitic plant lacking chlorophyll that derives nutrients from host plants.
40. Which of the following substances is not a constituent of a balanced diet?
Solution: Balanced diets include macronutrients (carbs, proteins, fats) and micronutrients (vitamins/minerals), but table salt (NaCl) is a mineral additive, not a core category.
1. Question 1
1. (a) (i) Define photosynthesis
(ii) Give two ways in which photosynthesis is important to animals
(b) Name three sources of chemical energy
(c) Describe how you would separate a mixture of sodium chloride and sand
(d) Complete and balance the following chemical reaction:
\[ \text{CaCO}_3 + \text{HCl} \rightarrow \]
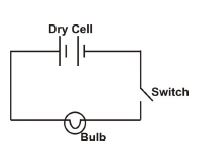
(e) Two dry cells, a switch and a bulb are connected in series. Draw and label a circuit diagram of the arrangement
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a) (i) Photosynthesis:
The process whereby green plants prepare food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll and light.
Or:
A process by which green plants turn carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen, using light energy trapped by chlorophyll.
(ii) Importance of photosynthesis to animals:
- Produces oxygen for respiration
- Produces food (carbohydrates) for nutrition
- Decreases the carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere to reduce pollution
(b) Sources of chemical energy:
- Car battery
- Electric cell
- Food (carbohydrates, fats, and oils)
- Fossil fuels (e.g., petrol, kerosene, coal)
(c) Separating sodium chloride and sand:
1. Add water to the mixture and stir to dissolve the salt.
2. Pour the mixture through filter paper in a funnel to separate sand (residue) from salt solution (filtrate).
3. Heat the salt solution to evaporate water, leaving salt crystals.
4. Dry the sand and salt obtained.
(d) \[ \text{CaCO}_3 + 2\text{HCl} \rightarrow \text{CaCl}_2 + \text{CO}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O} \]
(e) Circuit diagram:
2. QUESTION 2
2. (a) State two precautions that should be taken to prevent the spread of each of the following diseases:
(i) cholera
(ii) smallpox
(b) Describe how you would test for starch in a leaf.
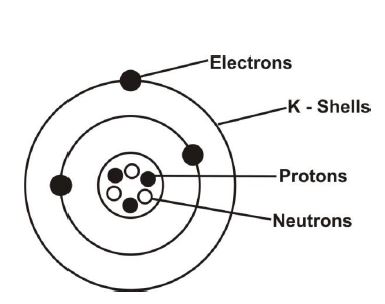
(c) Draw and label the structure of an atom containing three electrons. Indicate the charges of the particles.
(d) (i) Explain why an inclined plane is classified as a machine.
(ii) Give two reasons why the output energy of a machine is always less than the input energy.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a) (i) Cholera precautions:
- Eating hot meals
- Drinking clean potable water
- Washing hands with soap after toilet use
- Covering meals to prevent flies
- Keeping environment clean
- Covering rubbish bins properly
(ii) Smallpox precautions:
- Vaccination
- Quarantining patients
- Avoiding dusty areas
- Keeping clothes disinfected
- Ensuring room ventilation
(b) Test for starch in a leaf:
1. Boil leaf in water for 1 minute (kills cells).
2. Dip leaf in warm alcohol (removes chlorophyll).
3. Wash leaf in cold water (softens it).
4. Add iodine solution: Blue-black color indicates starch.
(c) Atom structure with three electrons:
(d) (i) Inclined plane is a machine because it reduces effort needed by increasing distance over which force is applied.
(ii) Reasons for output < input energy:
- Energy used to overcome friction
- Energy lost as heat
- Energy used to overcome gravity
---
3. QUESTION 3
3. (a) Name the two processes that lead to the formation of seeds in a flowering plant.
(b) (i) Give five components of blood.
(ii) State three functions of blood.
(c) (i) What is an electrical insulator?
(ii) Mention three examples of insulators.
(iii) Give two characteristics of an insulator that explain its behaviour.
(d) Classify the following substances under the three states of matter:
petrol, palm oil, soap, carbon dioxide, corn flour, smoke.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) Processes:
Pollination and fertilization.
(b) (i) Blood components:
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
- Platelets
- Dissolved nutrients (e.g., glucose)
- Metabolic waste (e.g., urea)
- Water
- Hormones
- Mineral salts
(ii) Blood functions:
- Transports oxygen to cells
- Removes metabolic waste (e.g., CO₂)
- Transports nutrients
- Maintains body temperature
- Protects against infections
- Transports hormones
- Forms clots to stop bleeding
(c) (i) Electrical insulator: Material that does not allow electric current to pass through.
(ii) Examples: Plastic, wood, rubber, glass, paper, fabric.
(iii) Characteristics:
- No free electrons
- High electrical resistivity
- Large energy gap between valence and conduction bands
(d) Classification:
- Solid: Soap, corn flour
- Liquid: Petrol, palm oil
- Gas: Carbon dioxide, smoke
---
4. QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) What is a deficiency disease?
(ii) Give two deficiency diseases and their causes.
(b) (i) State the importance of excretion in living organisms.
(ii) Name two excretory organs of the human body and the substances they excrete.
(c) (i) Explain why gases are more compressible than solids.
(ii) Give two areas where the compressible nature of a gas is applied.
(d) A piece of stone is dropped from a height to the ground. State the energies possessed by the stone:
(i) just before release;
(ii) midway during fall;
(iii) just before hitting ground.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) Deficiency disease: Illness caused by lack of essential nutrients.
(ii) Examples:
- Kwashiorkor (protein deficiency)
- Night blindness (vitamin A deficiency)
- Anaemia (iron deficiency)
- Rickets (vitamin D/calcium deficiency)
- Beriberi (vitamin B1 deficiency)
- Goitre (iodine deficiency)
- Scurvy (vitamin C deficiency)
(b) (i) Importance of excretion: Removes toxic waste to prevent bodily harm.
(ii) Excretory organs:
- Skin: Excretes sweat
- Lungs: Excrete CO₂
- Kidneys: Excrete urea
(c) (i) Gases are compressible because their molecules are widely spaced (vs. tightly packed solids), allowing reduction of volume under pressure.
(ii) Applications:
- Filling gas cylinders
- Using tyre pumps
- Inflating balloons
(d) Energies:
(i) Potential energy
(ii) Potential energy + kinetic energy
(iii) Kinetic energy